By Bizbuzzup
Introduction
In 2025, space is no longer just the domain of government agencies like NASA, ESA, or Roscosmos. A new era—Space Race 2.0—has emerged, driven by private companies, ambitious billionaires, and international competition. What was once a slow and costly venture is now fast, bold, and increasingly commercial.
From satellite mega-constellations and space tourism to lunar mining and Mars colonization, the space economy is growing exponentially. But with opportunity comes risk—space debris, militarization, and ethical dilemmas are serious concerns.
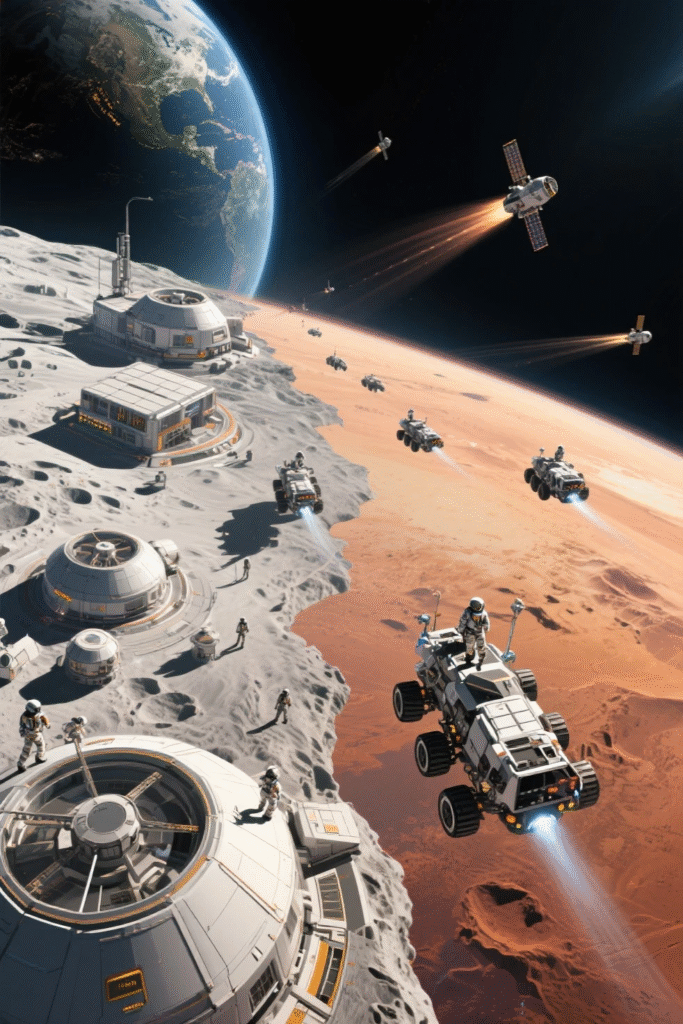
1. The New Players in the Space Race
- 🚀 SpaceX (USA): Elon Musk’s company is leading the charge with Starship, now regularly launching cargo to the Moon. Operates over 6,000 Starlink satellites, providing internet globally.
- 🛰️ Blue Origin (USA): Jeff Bezos’s Blue Moon lander completed its first cargo mission to the Moon in early 2025. Focused on building permanent infrastructure in orbit and beyond.
- 🇨🇳 CNSA (China): Successfully landed a robotic base module on the far side of the Moon. Developing nuclear-powered spacecraft for Mars missions.
- 🇪🇺 ESA (Europe): Partnering with startups to build sustainable launch pads. Contributing to the Artemis Accords and Moon Gateway missions.
- 🇮🇳 ISRO and Startups (India): Booming space economy with small satellite launches and plans for a space station by 2030. Startups like AgniKul and Skyroot gaining global traction.
2. Major Missions and Achievements in 2025
- NASA Artemis III: First woman and first person of color set to land on the Moon.
- SpaceX Starship: Completes first orbital refueling—key to Mars missions.
- Starlab: Construction begins on commercial space station.
- Asteroid Mining: NASA’s Psyche and private missions analyze resource-rich asteroids.
- Space Tourism: Over 1,000 civilians have now flown in space.
3. Opportunities in the Space Economy
The space industry is projected to exceed $1 trillion USD by 2030. Key sectors include:
- 🛰️ Satellite Services: Vital for communication, climate monitoring, and remote sensing.
- 🧳 Space Tourism: SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic offer zero-gravity trips (~$250,000).
- 🪐 Off-Earth Mining: Moon dust and asteroids rich in platinum and rare earths.
- 🌑 Colonization: Mars and Moon bases using AI, hydroponics, and 3D printing.
4. Risks and Ethical Challenges
- 💥 Space Debris: Over 100,000 pieces threaten spacecraft. Kessler Syndrome risk.
- ⚔️ Militarization: Nations testing anti-satellite weapons. Space becoming strategic domain.
- ⚖️ Legal Vacuum: 1967 treaty outdated. No laws for lunar mining or space property rights.
- 🌍 Inequality: Global South underrepresented. Risk of tech monopolies in orbit.
5. Global Collaboration or Cosmic Competition?
Two parallel tracks are shaping space in 2025:
Collaboration
- Artemis Accords promoting peaceful lunar exploration.
- Joint climate monitoring satellite networks.
- Multinational missions: Europe, India, Japan, Africa.
Competition
- U.S.–China race to establish Moon bases.
- Starlink vs. OneWeb in satellite internet dominance.
- Rising nationalism affecting tech sharing.
“The way we handle space exploration will define international relations in the 21st century.” — Prof. Joan Johnson-Freese
6. The Future: What Lies Beyond 2025
- Moon colonies by 2028.
- Mars flyby missions by 2030.
- AI space probes beyond the Kuiper Belt.
Critical technologies: reusable rockets, 3D habitats, radiation shields, and closed-loop systems. But legal frameworks and ethics will be just as vital.
Final Thoughts
Space Race 2.0 is about more than reaching planets—it’s about shaping our civilization. As nations and billionaires push the boundaries, we must ask:
Are we building an inclusive, peaceful future in space?
Or are we repeating the same inequalities, only higher up?
The choices we make now will echo across the stars.
Visit Bizbuzzup | External resources: Small Biz Trends, Detailed Top 50
By Bizbuzzup